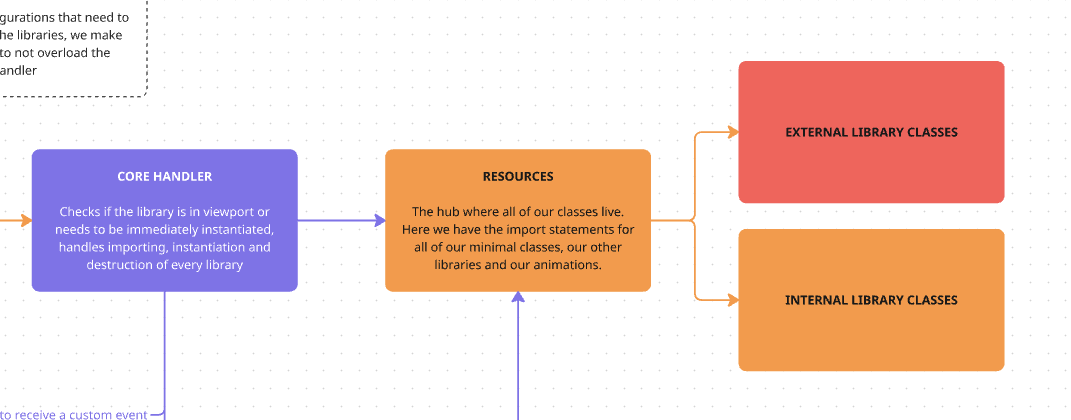
Resources
This is the file where all our import statements live, both for our libraries and our animations.
getAnimations
Section titled “getAnimations”This first array contains our proprietary libraries to add small animations to the page.
These classes are used in Project to be inserted into the GSAP timeline.
export const getAnimations = () => { return [ { name: "RevealIt", resource: async () => { const { default: RevealIt } = await import("@js/motion/modules/RevealIt.js"); return RevealIt; }, }, { name: "RevealStack", resource: async () => { const { default: RevealStack } = await import("@js/motion/modules/RevealStack.js"); return RevealStack; }, }, ];};getAutoAnimations
Section titled “getAutoAnimations”This one contains all our animation files. We use these mainly for heros. This array will then be used by our AssetManager.
These need to have the options object with a selector for our service to be able to locate them in the page and associate them to an HTML element.
export const getAutoAnimations = () => { return [ { name: "HeroA", resource: async () => { const { default: HeroA } = await import("@js/motion/hero/HeroA.js"); return HeroA; }, options: { selector: document.querySelector(".js--hero-a"), }, }, { name: "HeroB", resource: async () => { const { default: HeroB } = await import("@js/motion/hero/HeroB.js"); return HeroB; }, options: { selector: document.querySelector(".js--hero-b"), }, }, ];};getMinimal
Section titled “getMinimal”This is the array that contains all of the libraries that we need to have from the first moment we load a page, the ones that make the rest of our framework functional. They are used by the behind the scenes files, so you should not need to edit this section.
If you feel that there’s something that needs to be added here, contact your manager first.
export const getMinimal = () => { return [ { name: "isElementInViewport", resource: async () => { const { isElementInViewport } = await import("@terrahq/helpers/isElementInViewport"); return isElementInViewport; }, }, { name: "GSAP", resource: async () => { const module = await import("gsap"); return { ...module }; }, }, { name: "ScrollTrigger", resource: async () => { const { ScrollTrigger } = await import("gsap/ScrollTrigger"); return ScrollTrigger; }, }, { name: "Boostify", resource: async () => { const { default: Boostify } = await import("boostify"); return Boostify; }, }, { name: "digElement", resource: async () => { const { digElement } = await import("@terrahq/helpers/digElement"); return digElement; }, }, { name: "EventSystem", resource: async () => { const { default: EventSystem } = await import("@js/utilities/EventSystem"); return EventSystem; }, }, ];};getModules
Section titled “getModules”This is the main array of the file. Here is where you will add any libraries you want to implement in the project.
export const getModules = () => { return [ { name: "Marquee", resource: async () => { const { default: Marquee } = await import("@js/handler/marquee/Marquee"); return Marquee; }, }, { name: "Modal", resource: async () => { const { default: Modal } = await import("@terrahq/modal"); return Modal; }, }, ... ]}All libraries need to follow the same structure, where we have a name (that we will later use in our handlers to identify which resource we want to import) and the resource, which will contain the import statement for the library. It is important to know how the library will return its contents to assign them to the variable that we will later return.
These can also contain the options object, which accepts two properties:
{ name: "Collapsify", resource: async () => { const { default: Collapsify } = await import("@terrahq/collapsify"); return Collapsify; }, options: { modifyHeight: true, condition: async () => { const {u_is_touch} = await import('@andresclua/jsutil'); return !u_is_touch() }, },},modifyHeightto mark the library as one that modifies the height of the page when loadedcondition, a callback that, whenfalse, allows us to skip the library when loading the page. For instance, if we want to load some libraries only in desktop.
loadLibrary
Section titled “loadLibrary”This file also contains the loadLibrary method that is explained in our CoreHandler page, and that is in charge of executing the import statement and returning the final contents of the library to our framework.
export const loadLibrary = async (payload) => { const { libraryName } = payload;
const modules = getModules(); const library = modules.filter((mod) => mod.name == libraryName)[0]; if (library?.options?.condition && typeof library?.options?.condition == "function") { const shouldLoad = await library.options?.condition(); if (shouldLoad === false) { return; } } return library;};Knowledge Check
Test your understanding of this section
Loading questions...